- History of Machine Tools: From the Industrial Revolution to Smart Manufacturing Systems
- Early Developments: From Hand Tools to Machines
- The Industrial Revolution: The Birth of Modern Machine Tools
- James Nasmyth and Steam Hammers
- The Rise of Electricity and Automation
- William Sellers and the American Standard
- Today and the Future: Digitalization and Smart Systems
- Conclusion
1. History of Machine Tools: From the Industrial Revolution to Smart Manufacturing Systems
The history of machine tools reflects a developmental journey shaped by groundbreaking inventions and the contributions of visionary engineers in the fields of mechanical engineering and industry. These machines have evolved from simple hand tools to today’s complex and intelligent systems.
2. Early Developments: From Hand Tools to Machines
The origins of machine tools can be traced back to the simple tools used by ancient civilizations to work with stone and wood. Manually operated lathes from the Egyptian and Roman periods are among the earliest known examples. However, the birth of modern machine tools occurred during the Industrial Revolution. The advent of steam power and advancements in metalworking techniques led to the development of more complex and efficient machines.
3. The Industrial Revolution: The Birth of Modern Machine Tools
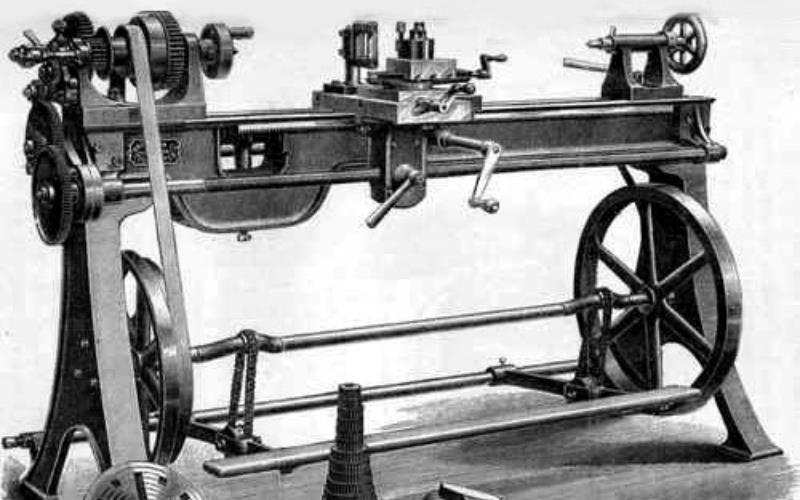
Towards the end of the 18th century, the Industrial Revolution accelerated the development of machine tools. During this time, Henry Maudslay emerged as a pivotal figure with the invention of the modern lathe. In 1797, he introduced the leadscrew system, which allowed for precise machining of metal components and revolutionized manufacturing. His invention paved the way for mass production and standardization.
Another notable figure of this era was Joseph Whitworth, who in 1841 developed the "Whitworth thread standard," ensuring compatibility of screws and fasteners used across the industry. Whitworth also contributed to the development of surface grinding machines and other precision tools.
4. James Nasmyth and Steam Hammers
In the mid-19th century, James Nasmyth played a key role in the advancement of machine tools. In 1839, he invented the steam hammer—a major innovation in metalworking. His invention enabled the precise forging of large and heavy metal components, transforming the forging process in industrial settings.
5. The Rise of Electricity and Automation
The early 20th century marked a new era where machine tools became even more efficient through the use of electric power. Electric motors allowed machines to operate with greater precision, strength, and control. During this time, Richard Roberts developed the gear-cutting milling machine, enhancing the complexity and reliability of these tools. This period also saw the development of Numerical Control (NC) and later Computer Numerical Control (CNC) systems, which revolutionized manufacturing by enabling automated and highly precise operations.
6. William Sellers and the American Standard
American engineer William Sellers introduced the American Standard screw thread system in 1864, establishing critical industrial standards in the United States. Sellers contributed to the modernization of machine tool design and manufacturing, leading to more efficient production processes across the country.
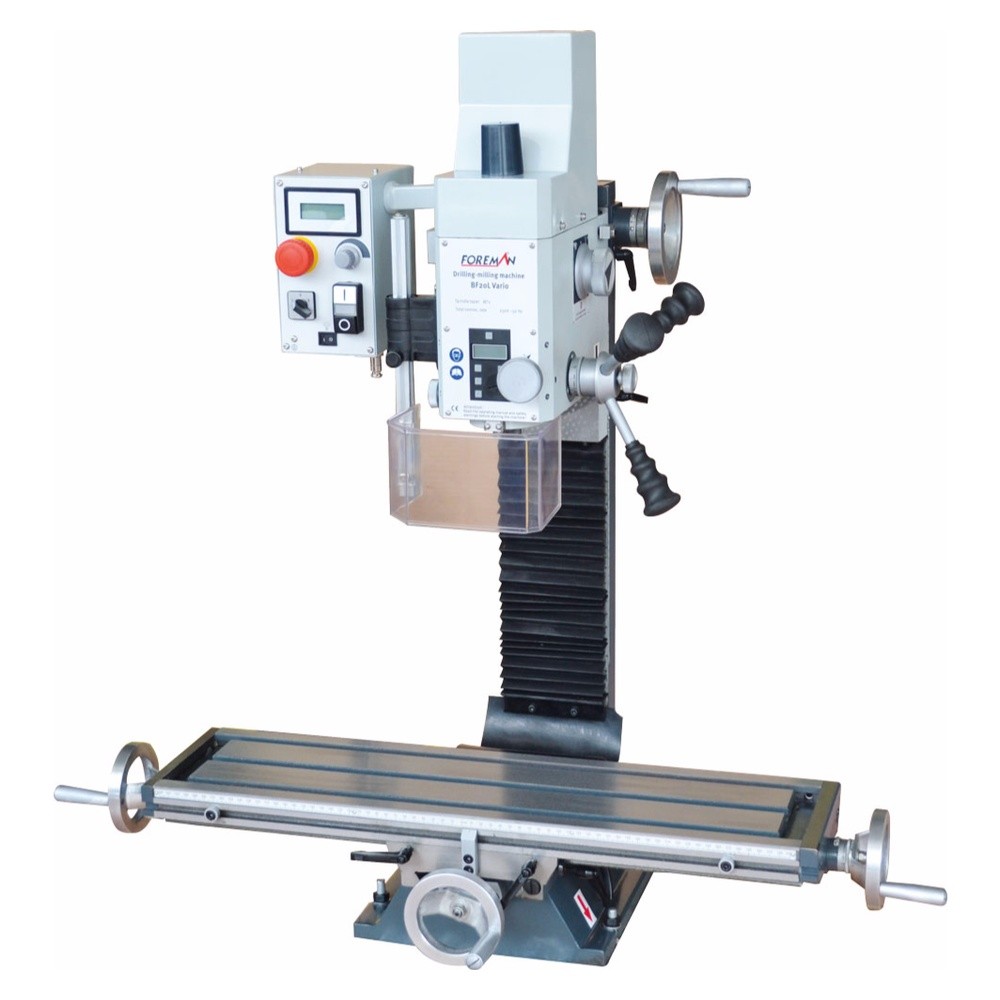
7. Today and the Future: Digitalization and Smart Systems
Today’s machine tools have been further enhanced by digital technologies and smart manufacturing systems. Concepts like Industry 4.0, IoT, and artificial intelligence have made these machines more efficient and flexible within production environments. Smart machine tools are equipped with features such as condition monitoring, predictive maintenance, and automated optimization—playing a central role in modern manufacturing.
8. Conclusion
The history of machine tools has been shaped by groundbreaking innovations and the genius of great inventors. The contributions of Henry Maudslay, Joseph Whitworth, James Nasmyth, and others laid the foundation for modern manufacturing technologies and significantly advanced industrial production. Machine tools such as lathes, milling machines, drills, and grinders have evolved from simple hand tools into cutting-edge systems. The future promises even smarter, more adaptable, and more efficient machine tools that will continue to revolutionize manufacturing.

















































_zkmmzopp1k.jpg)